Table of Contents
ToggleHepatitis C: The Silent Epidemic and the Fight to Eradicate It
Often termed a ‘silent epidemic,’ Hepatitis C affects millions globally. In this blog post, we seek to understand Hepatitis C, exploring its impact and the ongoing efforts to eradicate it.
Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a viral infection that primarily affects the liver.
The Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is blood-borne, commonly transmitted through direct contact with the blood of a person who has the infection.
This can occur through sharing needles, syringes or needlestick injuries in healthcare settings and through sexual contact.
The disease can be ‘acute,’ a short-term illness occurring within the first six months after exposure to the virus or ‘chronic,’ a long-term illness that occurs when the virus remains in a person’s body.
Chronic HCV can lead to severe health problems such as liver failure and liver cancer.
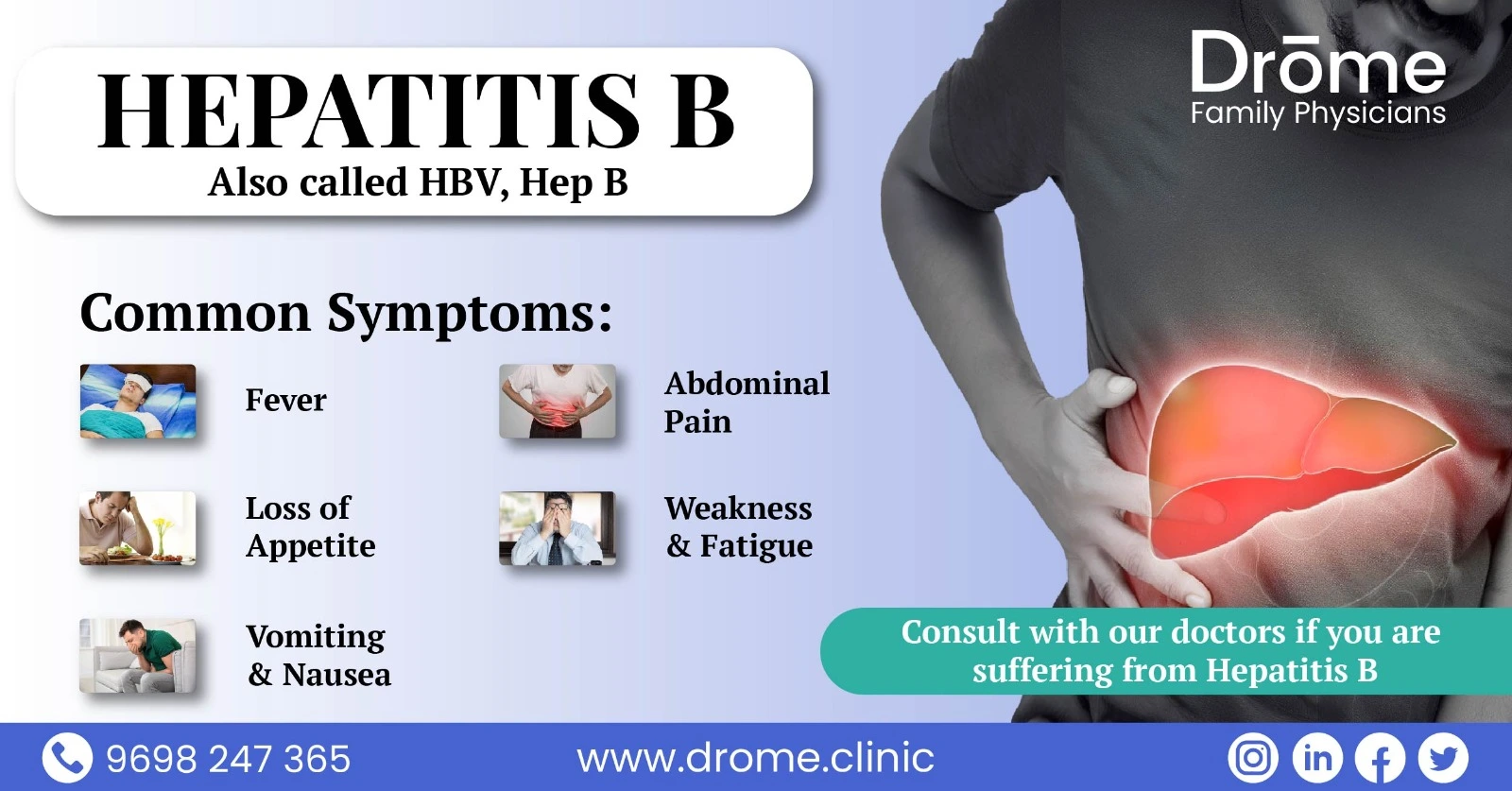
Hepatitis C infection can present with fever, jaundice, fatigue, vomiting.
The Silent Epidemic
Many people with HCV are unaware they have the virus because they may not look or feel sick.
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that nearly 71 million people globally have chronic Hepatitis C but a significant number of these individuals are unaware of their status.
As a result they do not seek treatment, allowing the disease to progress and unknowingly transmitting the virus to others.
The Quest for Eradication
Significant developments have been made in the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of HCV, that have put the goal of its eradication within reach.
1. Improved Testing and Diagnosis: Rapid diagnostic tests which provide diagnosis in a single visit are becoming more widely available..
2. Newer Treatment Options: The past decade has seen a revolution in Hepatitis C treatment with the introduction of direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) which can be cure Hepatitis C in more than 95% of cases and with fewer side effects than previous treatments.
3. Preventive Measures: Measures such as safe injection practices and blood safety play a crucial role in preventing Hepatitis C transmission.
4. Global Health Initiatives: The World Health Organization’s Global Health Sector Strategy on Viral Hepatitis aims to eliminate viral hepatitis as a major public health threat by 2030. This strategy sets targets for prevention, treatment and mortality reduction.
The Challenges Ahead
Despite the advancements, numerous challenges persist in eradicating Hepatitis C.
These include the lack of awareness about the disease, inadequate access to testing and treatment, social stigma and the high cost of new treatments (particularly in low and middle-income countries).
Addressing these challenges requires collaborative efforts, political will and investment in public health infrastructure and education.
For more updates visit: drome.clinic or drome.co.in