Table of Contents
ToggleGastritis: Understanding, Managing, and Preventing Stomach Inflammation
Gastritis: A reminder that our gut health is a mirror of our lifestyle choices, urging us towards a path of care and balance.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on gastritis, a common but often misunderstood condition affecting the stomach lining. This blog aims to provide valuable insights into the causes, symptoms, treatments and preventive measures for gastritis, helping you manage or avoid this condition effectively.
What Is Gastritis?
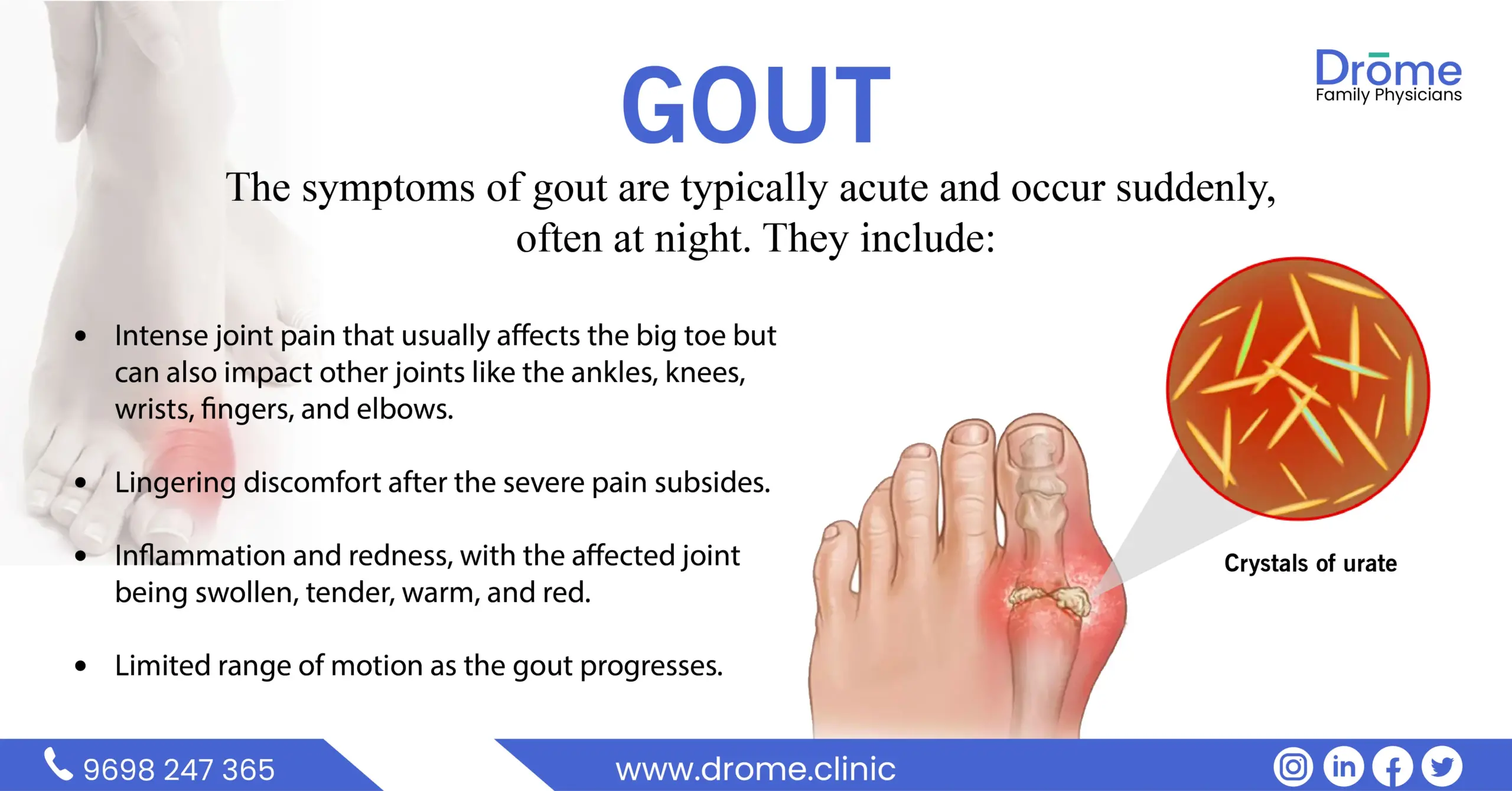
Gastritis is an inflammation of the stomach lining.This lining (a soft tissue called mucosa) protects the stomach from the acids, enzymes and microorganisms that pass through it every day.
Types
Types: Gastritis is classified into 2 types based on its cause:
Acute: It is sudden and temporary. The conditions that cause it are also acute
Chronic: It is a long-term condition. It tends to develop gradually, as a result of another chronic condition
Gastritis may be classified on the cause. Some examples are:
- Infectious gastritis.
- Drug-induced gastritis.
- Alcohol-induced gastritis.
- Stress-induced gastritis
Causes of Stomach Inflammation:
Gastritis may be caused by various conditions. Commonly it is due to-
Infections: They are among the most common causes of gastritis, especially acute gastritis. Bacterial infections, viral infections and fungal infections can all cause acute or chronic gastritis. H. pylori infection is a common, chronic bacterial infection that can cause chronic gastritis.
Chemicals: Alcohol and certain drugs can cause chemical erosion of the stomach lining (erosive gastritis)
Overuse of NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), such as aspirin and ibuprofen, is one of the most common causes of acute gastritis.
Autoimmune diseases: The immune system mistakenly attacks body’s own cells with inflammation,leading to chronic gastritis.
Reduced blood supply: Major surgery, trauma or critical illness can cause acute gastritis.
Other causes :
- Radiation therapy (mucositis).
- Chemotherapy.
Symptoms
There might not be any noticeable symptoms due to gastritis. However if there are symptoms, it may mean that it’s more severe or it’s been going on for a long time.
Symptoms can range from mild to severe and include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Upper abdominal pain or discomfort
- Indigestion
- Loss of appetite
- Bloating and belching
In severe cases, bleeding of the stomach lining-this may present as
- Black blood in stools
- Vomiting of black blood
Diagnosis & Treatment
Diagnosis
Diagnosing gastritis involves:
- A review of medical history and symptoms.
- Endoscopy with biopsies for definitive diagnosis.
- Blood tests, stool tests, or breath tests for H. pylori.
Treatment
Treatment depends on the cause and severity.
- Cases of acute gastritis recover after the acute cause goes away.
Chronic gastritis needs treatment for cure. The treatment depends on the cause and may include-
- Antibiotics and other medications to treat H. pylori infection
- Using alternative medications for conditions being treated treating with NSAIDs.
- Addiction treatment services for alcohol use disorder
- Targeted drugs for autoimmune diseases.
- In rare cases, surgery to fix gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding, ischemia or bile reflux.
- Prescription acid-blocking medications to promote healing.
Fast relief from gastritis can be achieved by over-the-counter (OTC) medications that soothe irritation and neutralize stomach acid, like proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)
Conclusion
Gastritis, while common, should not be taken lightly. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is key to managing this condition effectively and maintaining good digestive health.
Yes, chronic stress is a known trigger for gastritis as it can lead to an increase in stomach acid production.
Gastritis itself is not contagious but the H. pylori infection, a common cause of gastritis, spreads by the fecal-to-oral route.You can help prevent spreading infections by practicing good hygiene, such as handwashing after going to the bathroom and before handling food.
Yes, dietary changes can play a significant role in managing gastritis. Avoiding spicy, acidic, or fatty foods can help reduce symptoms.
Treatment can effectively manage or relieve symptoms, but some forms of chronic gastritis may require ongoing management.
Sourced from the Cleveland Clinic