Table of Contents
ToggleBehind the Earache: Decoding the Mysteries of Ear Infections
An ear infection may start silently, but it certainly doesn’t stay quiet. Timely intervention is key to restoring the symphony of health.
Ear Infection
The world of health and wellness is vast and complex. Amongst the myriad of condition, acute ear infection are a recurring concern for many, especially parents of young children. Delving deeper into this topic, we bring you a detailed overview.
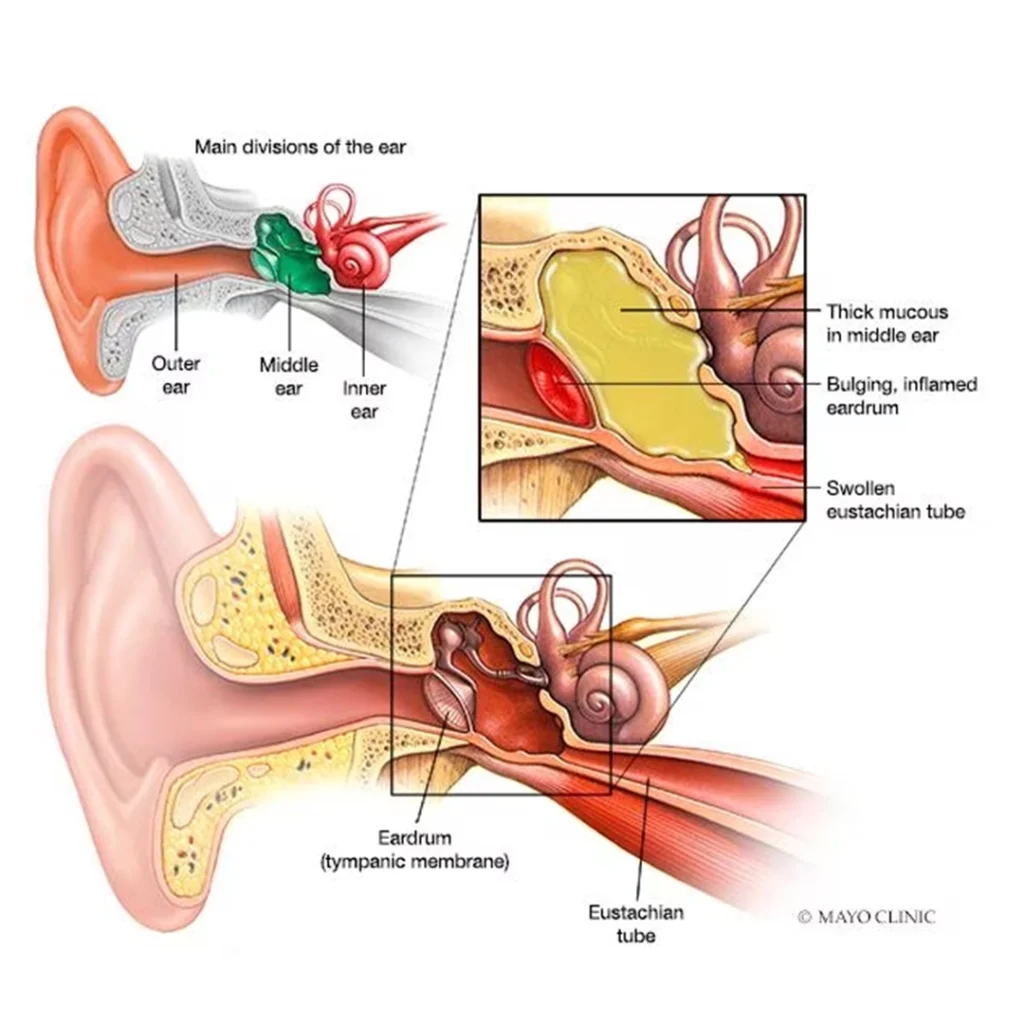
Overview of Ear Infection
Ear infection, although common, can be a source of distress and discomfort, predominantly in children. These infection arise when the ear becomes a battleground, invaded by bacterial or viral agents leading to inflammation and a troubling build-up of fluids.
Ear Infection: The Basics
To understand ear infection better, it’s essential to know the ear’s structure. It’s divided into three distinct parts:
- The outer ear, which captures sound waves.
- The middle ear, where acute infection usually occur. This area, located behind the eardrum, is vital for transmitting sound from the outer to the inner ear.
- The inner ear, which plays roles in both hearing and balance.
An acute ear infection, scientifically termed as Acute Otitis Media (AOM), primarily focuses its wrath on the middle ear, causing painful symptoms.
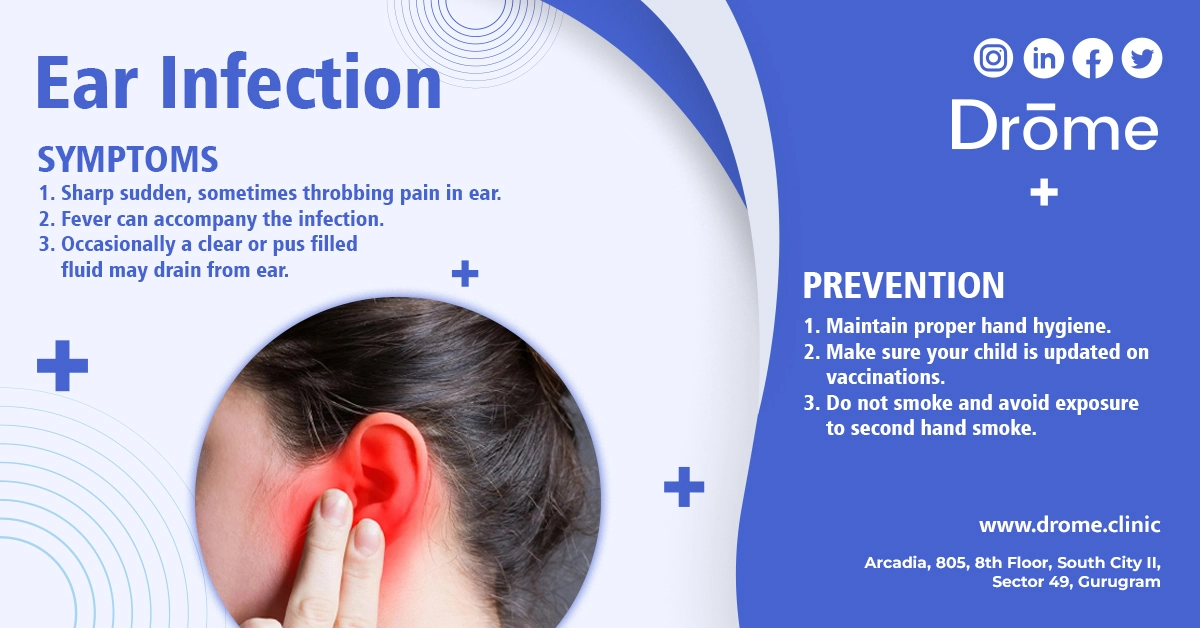
Ear Infection Symptoms and Causes: What to watch out for
Symptoms of Ear Infection are multifaceted:
- A sharp, sudden, sometimes throbbing pain in the ear.
- Hearing might become muffled or reduced.
- Occasionally, a clear or pus-filled fluid may drain from the ear.
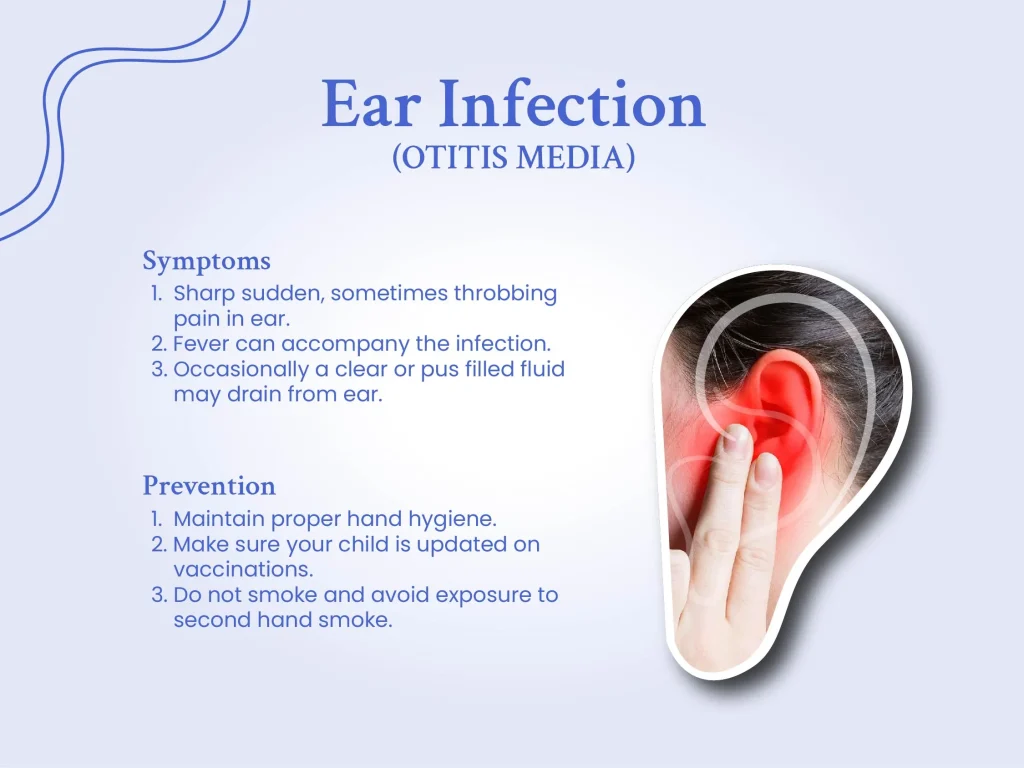
- Fever can accompany the infection, making one feel even more under the weather.
- In children, irritability, fussiness, and even nausea or vomiting can be evident.
- Adults might experience dizziness or a persistent feeling of fullness in the ear.
Causes range from the simple to the complex:
- Infections: Often, bacterial and viral infections originating from illnesses like colds or the flu can migrate to the ear.
- Eustachian Tube Dysfunction: This crucial tube balances air pressure in the middle ear. If it gets blocked or doesn’t function properly, fluid accumulation can occur, creating a ripe environment for infections.
Risk: Who’s More Susceptible?
Certain populations and conditions amplify the risk:
- Age Factor: Children, especially those between 6 months to 2 years, have Eustachian tubes that are shorter and more horizontal, increasing susceptibility.
- Environmental Factors: Children in group child care or daycare settings encounter a wider variety of germs.
- Seasonal Contributors: For reasons not entirely clear, ear infections spike in the fall and winter months.
- Air Quality: Chronic exposure to tobacco smoke or polluted environments can irritate and inflame the Eustachian tubes.
Complications: Beyond the Immediate Concern
When AOM goes untreated or isn’t managed effectively, it can result in:
- Hearing Impairment: Though generally temporary, it’s distressing. Repeated infections can even lead to mild permanent hearing loss.
- Infection’s Wrath: The microbes can be relentless, spreading to adjacent tissues, potentially leading to more severe conditions like mastoiditis.
- Eardrum Turmoil: Repeated onslaughts can cause the eardrum to rupture or lead to cholesteatoma, a cystic growth in the middle ear.
Ear Infection Treatment: Paths to Healing
Fortunately, AOM is treatable:
- Watchful Waiting: Not every infection mandates aggressive treatment. Some may resolve without intervention, but observation is key.
- Pain Alleviation: Over-the-counter pain relievers, when used appropriately, can be a boon.
- Antibiotics: Reserved for severe infections or cases showing no improvement, and it’s imperative to complete the course.
- Warm Compress: A simple yet effective remedy for pain.
- Surgical Intervention: In chronic cases, a procedure to place tubes in the ears might be recommended to prevent fluid accumulation.
Ear Infection Prevention: A Proactive Approach
Being proactive can significantly reduce occurrences:
- Vaccinations: Regular vaccinations fortify against many bacteria and viruses that can lead to AOM.
- Hygiene: The simple act of regular handwashing can be a game-changer.
- Nutrition: Breastfeeding infants can offer added immunity against ear infections.
- Environment: Keeping away from smokers and ensuring a clean living environment minimizes risks.
- Allergy Management: If one suffers from allergies, managing them effectively can prevent Eustachian tube blockage.
Conclusion
While acute ear infection can be distressing, with a comprehensive understanding and proactive approach, they are largely manageable and often preventable. Always prioritize professional medical advice for diagnosis and treatment. Knowledge, as they say, is power – and in this case, the power to heal.
For more blog: drome.clinic/blog