Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Hyperthyroidism: A Guide for the Indian Population
In India, where diverse diets and lifestyles significantly impact health, understanding conditions like hyperthyroidism is crucial. This write-up aims to shed light on hyperthyroidism, its symptoms, causes, treatments, and ways to manage or prevent it, tailored to the Indian context.
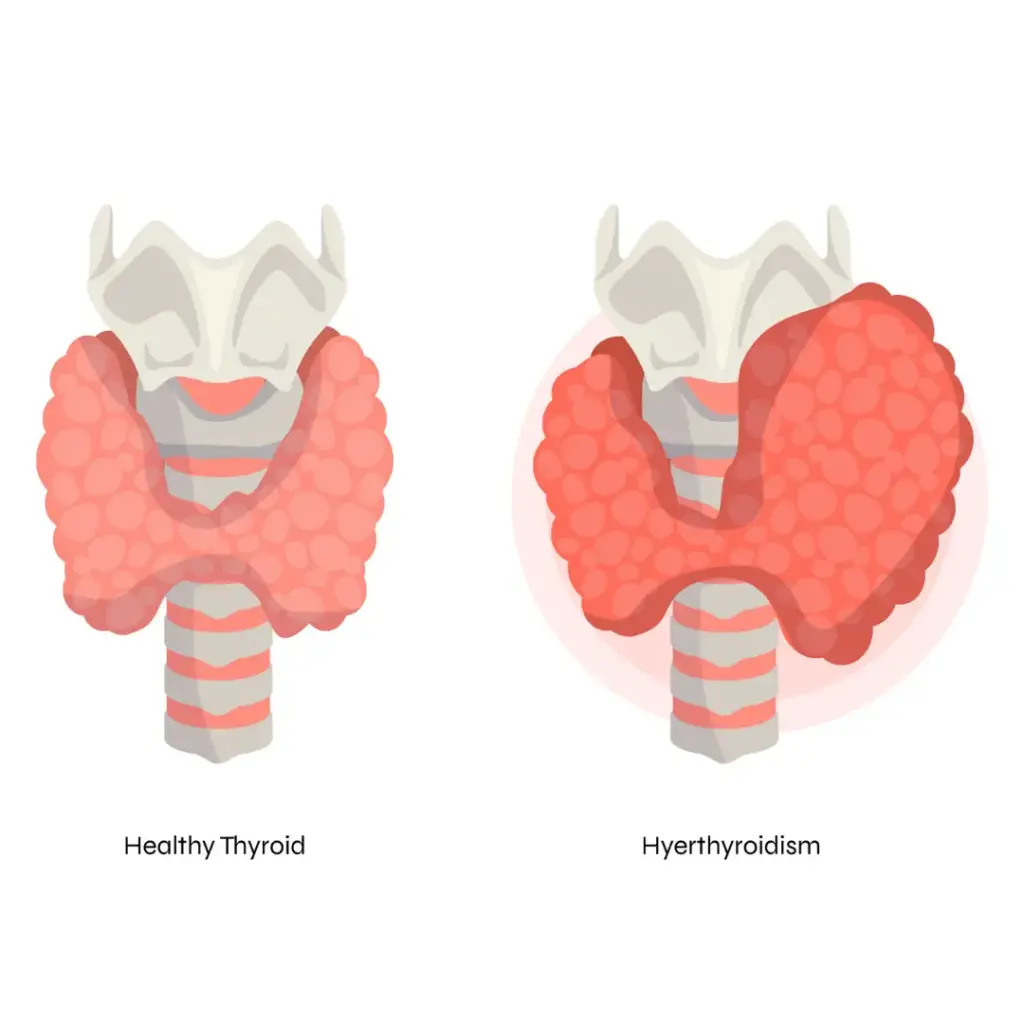
What is Hyperthyroidism?
Hyperthyroidism, also known as overactive thyroid, is a condition where the thyroid gland produces excessive thyroid hormones. These hormones play vital roles in regulating metabolism, heart rate, and body temperature. An imbalance can have widespread effects on the body.
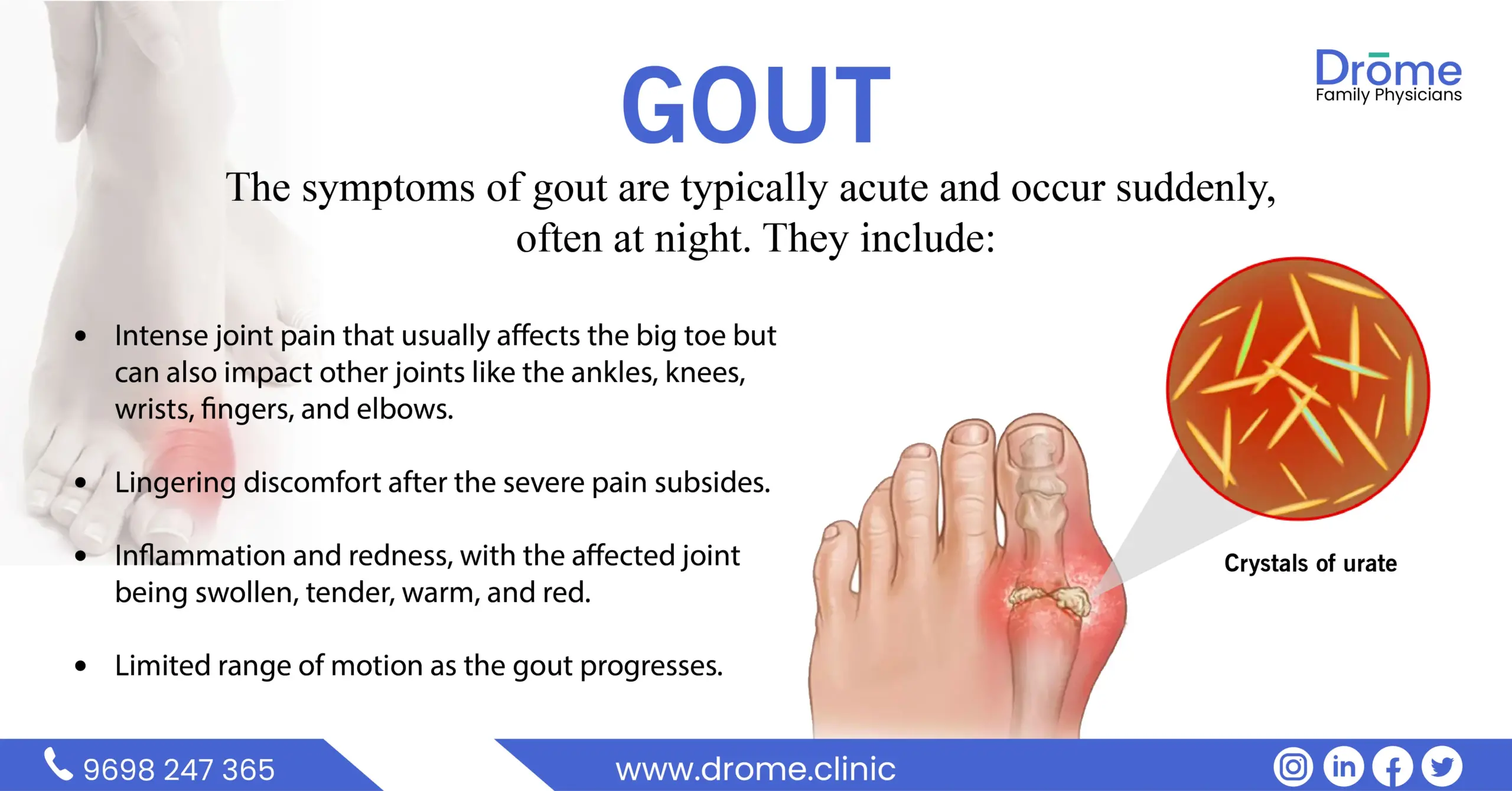
Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism
The symptoms can be subtle or mimic other health issues, making early detection challenging. They include:
- Unexpected weight loss, even when appetite and food intake remain the same or increase
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Increased appetite
- Nervousness, anxiety, and irritability
- Sweating and sensitivity to high temperatures
- More frequent bowel movements
- Fatigue and muscle weakness
- Difficulty sleeping
Causes of Hyperthyroidism
Several factors can lead to hyperthyroidism, including:
Graves’ Disease: An autoimmune disorder and the most common cause in India.
Thyroid Nodules: Lumps in the thyroid gland can become overactive.
Thyroiditis: Inflammation of the thyroid, which can cause temporary hyperthyroidism.
Excessive Iodine Intake: From diet or medications, since iodine is crucial for thyroid hormone production.
Diagnosis of Hyperthyroidism
Early diagnosis is key. If you suspect hyperthyroidism, a doctor can confirm it through:
- Blood tests to measure levels of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) and TSH
- Radioiodine uptake test
- Thyroid scan
- Ultrasound of the thyroid
Treatment and Management
Treatment varies based on the cause, severity, and the patient’s overall health, including:
Medications: To reduce thyroid hormone production or its effects on the body.
Radioactive Iodine Therapy: A common and effective treatment that destroys overactive thyroid cells.
Surgery: Removal of the thyroid gland, necessitating lifelong hormone replacement therapy.
Prevention and Risk Factors
While genetic factors can’t be altered, understanding risk factors can help in prevention:
- Autoimmune Diseases: Such as Graves’ disease, are significant risk factors.
- Sex and Age: Women and older adults are more likely to develop hyperthyroidism.
- Diet: Adequate iodine intake is essential; too much or too little can be harmful.
Conclusion
Hyperthyroidism is a manageable condition with timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Awareness and understanding of the symptoms, risk factors, and treatments can help individuals lead healthier lives. Regular check-ups and consultations with healthcare providers are vital, especially if you have risk factors for thyroid diseases.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can diet affect hyperthyroidism?
Yes, diet plays a role, especially iodine intake. Consult a healthcare provider for dietary advice tailored to your condition.
While there’s no cure for autoimmune causes like Graves’ disease, treatments are available to effectively manage and control symptoms.
Can stress cause hyperthyroidism?
Stress alone doesn’t cause hyperthyroidism but can exacerbate symptoms and trigger conditions like Graves’ disease.
How does hyperthyroidism affect pregnancy?
It can lead to complications such as premature birth and preeclampsia. It’s crucial for pregnant women with hyperthyroidism to be closely monitored.