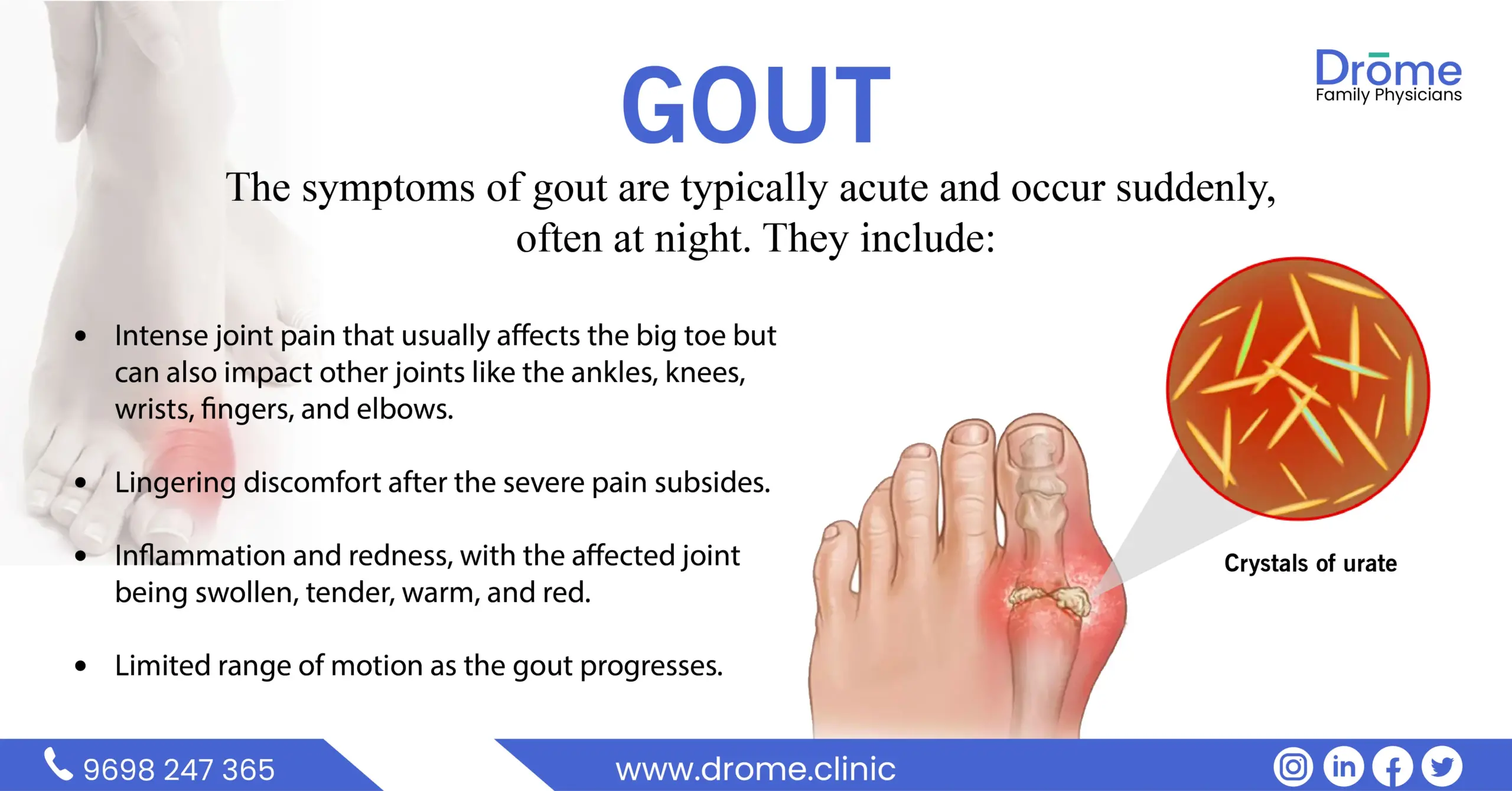
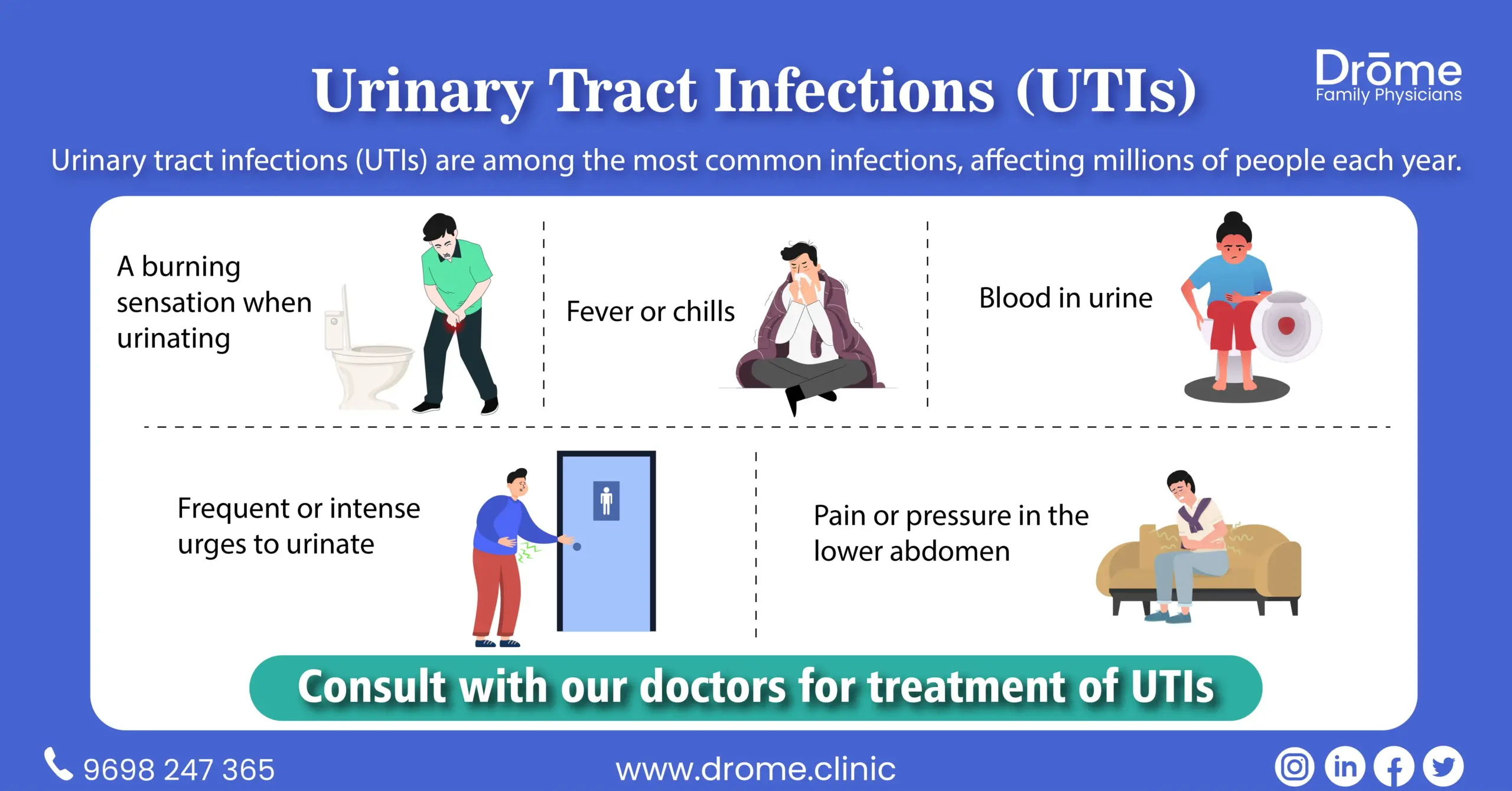
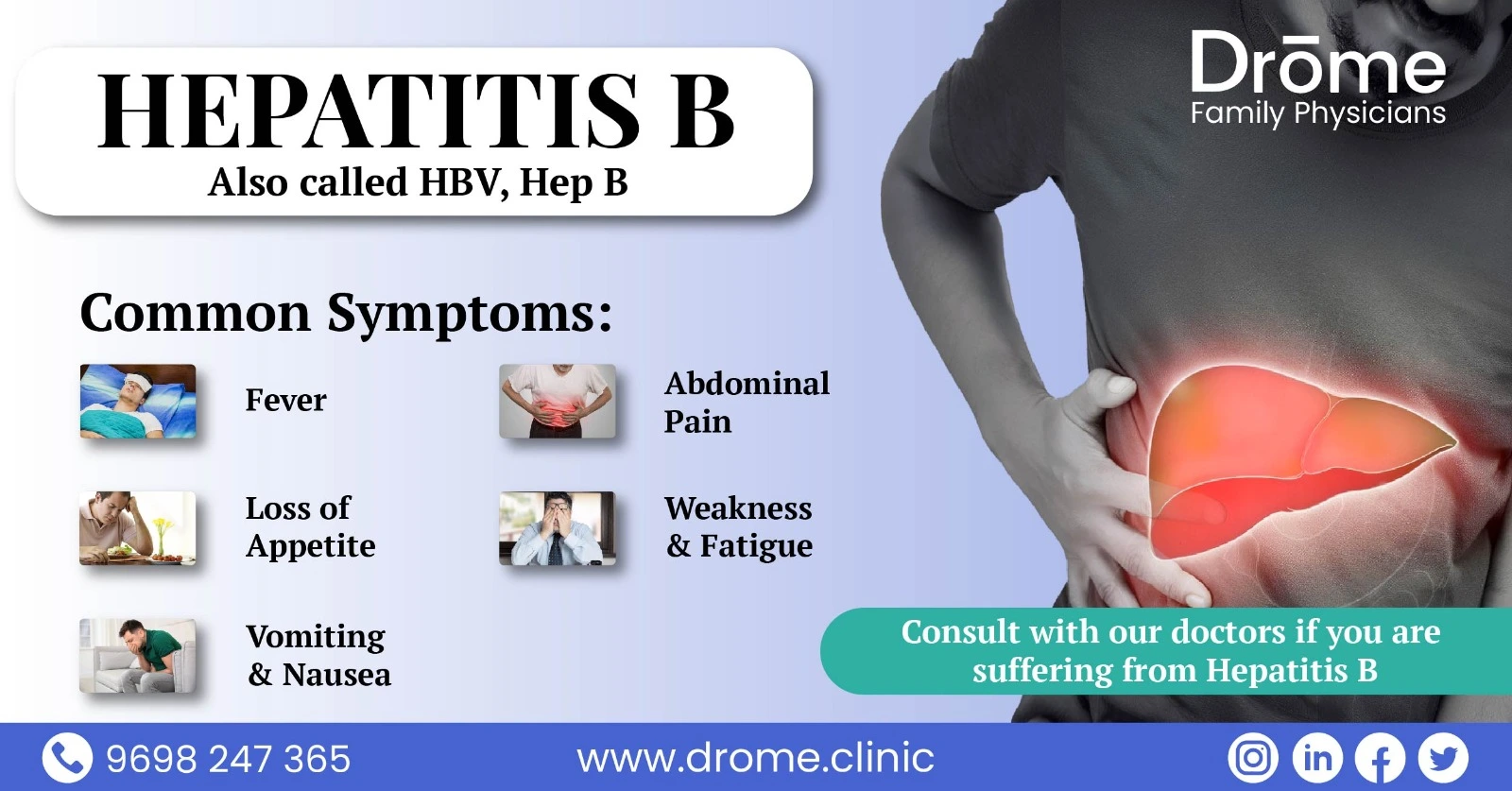
Table of Contents
ToggleChronic Complications of Diabetes
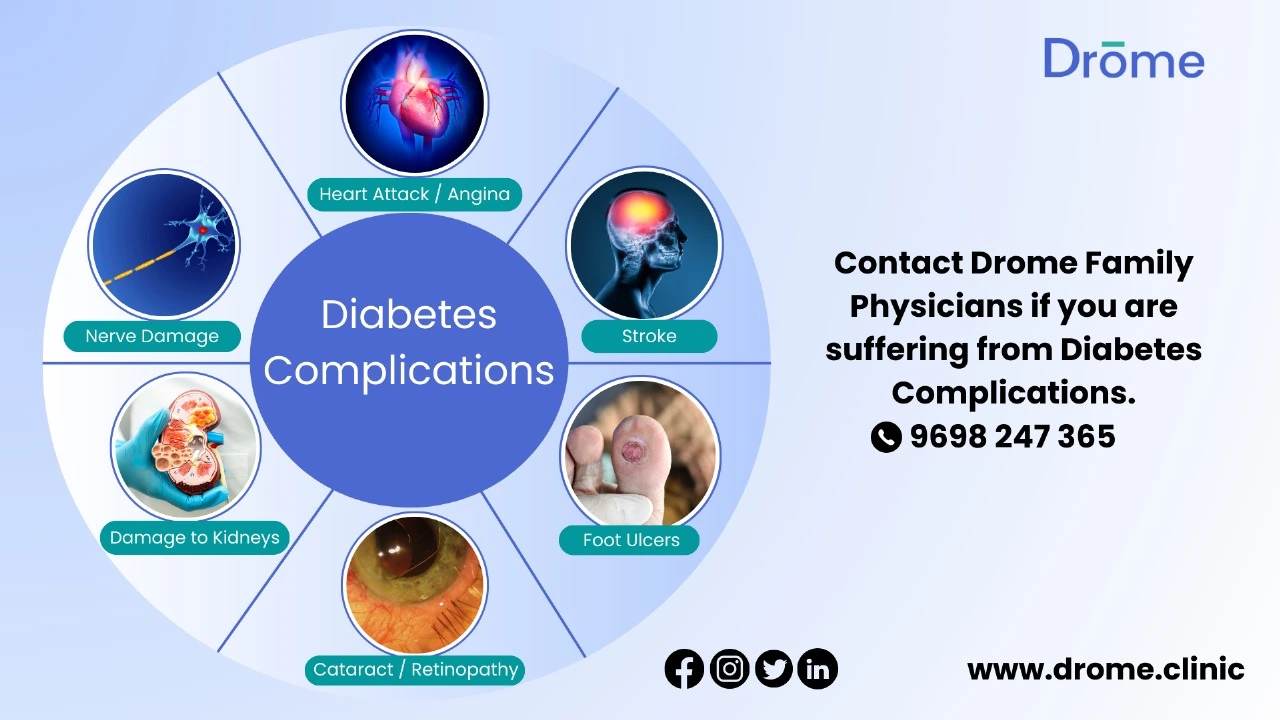
Diabetes is a complex chronic condition that, if not managed properly, can lead to a range of severe health complications. It is vital for individuals living with diabetes to understand these potential risks in order to take proactive measures to prevent them. Here’s a closer look at some of the major complications associated with diabetes:
Cardiovascular Disease
Diabetes significantly increases the risk of various cardiovascular problems, including coronary artery disease with chest pain (angina), heart attack, stroke, and narrowing of arteries (atherosclerosis). High blood sugar levels can lead to the buildup of plaques in blood vessels, eventually leading to cardiovascular disease.
Nerve Damage (Neuropathy)
Excess sugar can injure the walls of the tiny blood vessels (capillaries) that nourish the nerves, especially in the legs. This can cause tingling, numbness, burning, or pain that usually begins at the tips of the toes or fingers and gradually spreads upwards. Damage to the nerves related to digestion can cause problems with nausea, vomiting, diarrhea or constipation
Kidney Damage (Nephropathy)
The kidneys contain millions of tiny blood vessel clusters that filter waste from the blood. Diabetes can damage this delicate filtering system leading to kidney failure or irreversible end-stage kidney disease, which may require dialysis or a kidney transplant.
Eye Damage
Diabetes can damage the blood vessels of the retina (diabetic retinopathy), potentially leading to blindness. Diabetes also increases the risk of other serious vision conditions, such as cataracts and glaucoma.
Foot Damage
Nerve damage in the feet or poor blood flow to the feet increases the risk of various foot complications. Left untreated, cuts and blisters can develop serious infections, which often heal poorly. These infections may ultimately require toe, foot, or leg amputation.
Skin Conditions
Diabetes may leave you more susceptible to skin problems, including bacterial and fungal infections.
Hearing Impairment
Hearing problems are more common in people with diabetes, likely due to the damage high glucose levels can do to blood vessels and nerves.
Conclusion
While diabetes can lead to numerous health issues, effectively managing the condition reduces the risk of developing these serious complications. Understanding these potential risks is the first step in maintaining a healthy, active life despite diabetes. Managing blood sugar levels, maintaining a healthy diet, regular physical activity, and proper medication adherence are crucial in preventing or delaying these diabetes-related complications.